CD39 TME缺氧诱发肿瘤逃逸关键蛋白
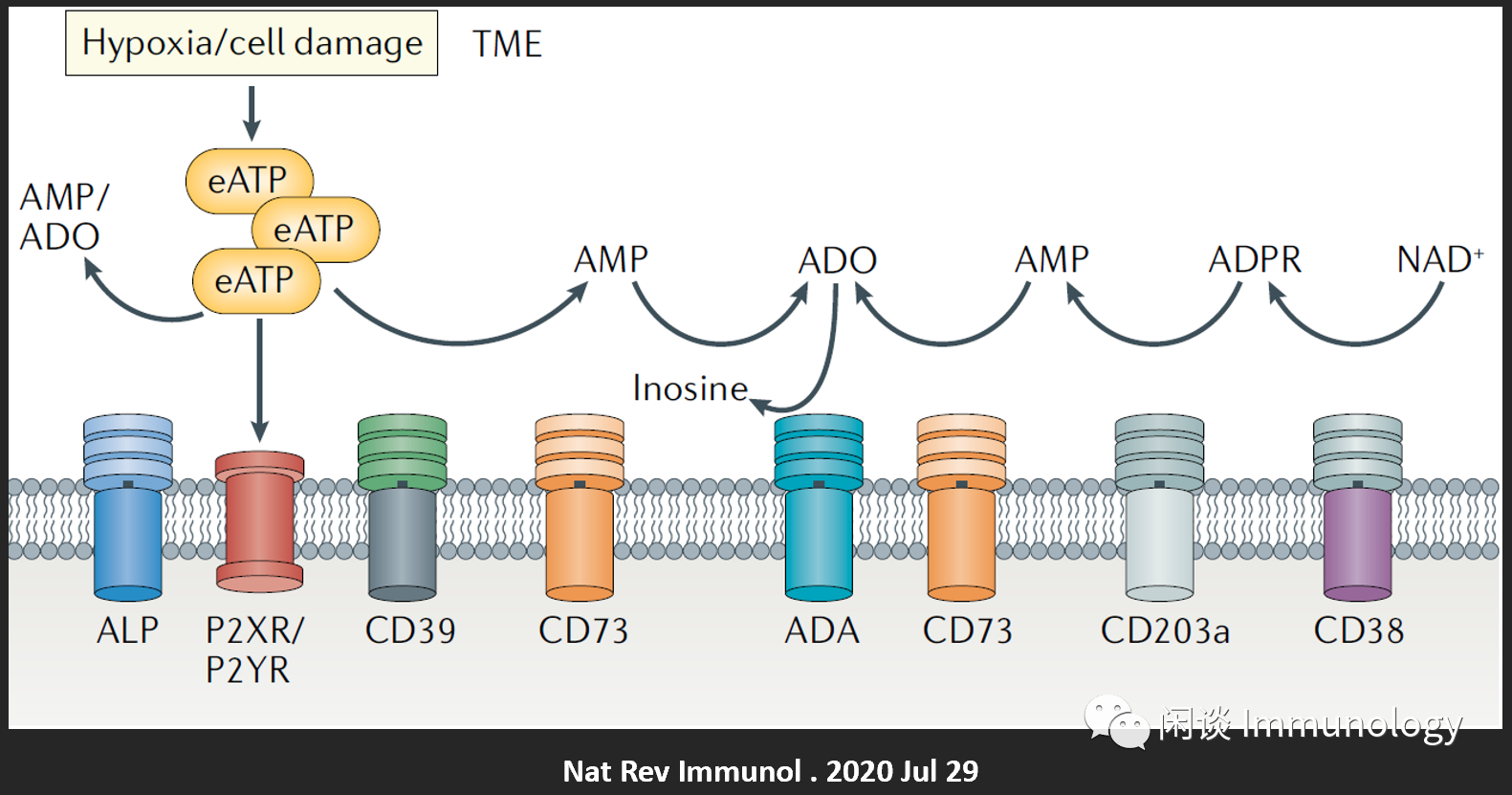
CD39是一种细胞膜蛋白,属于胞外核苷酸三磷酸盐二磷酸水解酶(ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1; encoded by ENTPD1)家族,具有ATP酶和二磷酸腺苷(ADP)酶活性,将胞外ATP和ADP水解为单磷酸腺苷(AMP)。CD73则将AMP水解为腺苷。
表达
广泛表达于免疫细胞;非免疫细胞;肿瘤细胞。
缺氧,应激或死亡细胞释放ATP,提供炎症信号,是有效启动先天免疫和适应性免疫反应的关键因素。
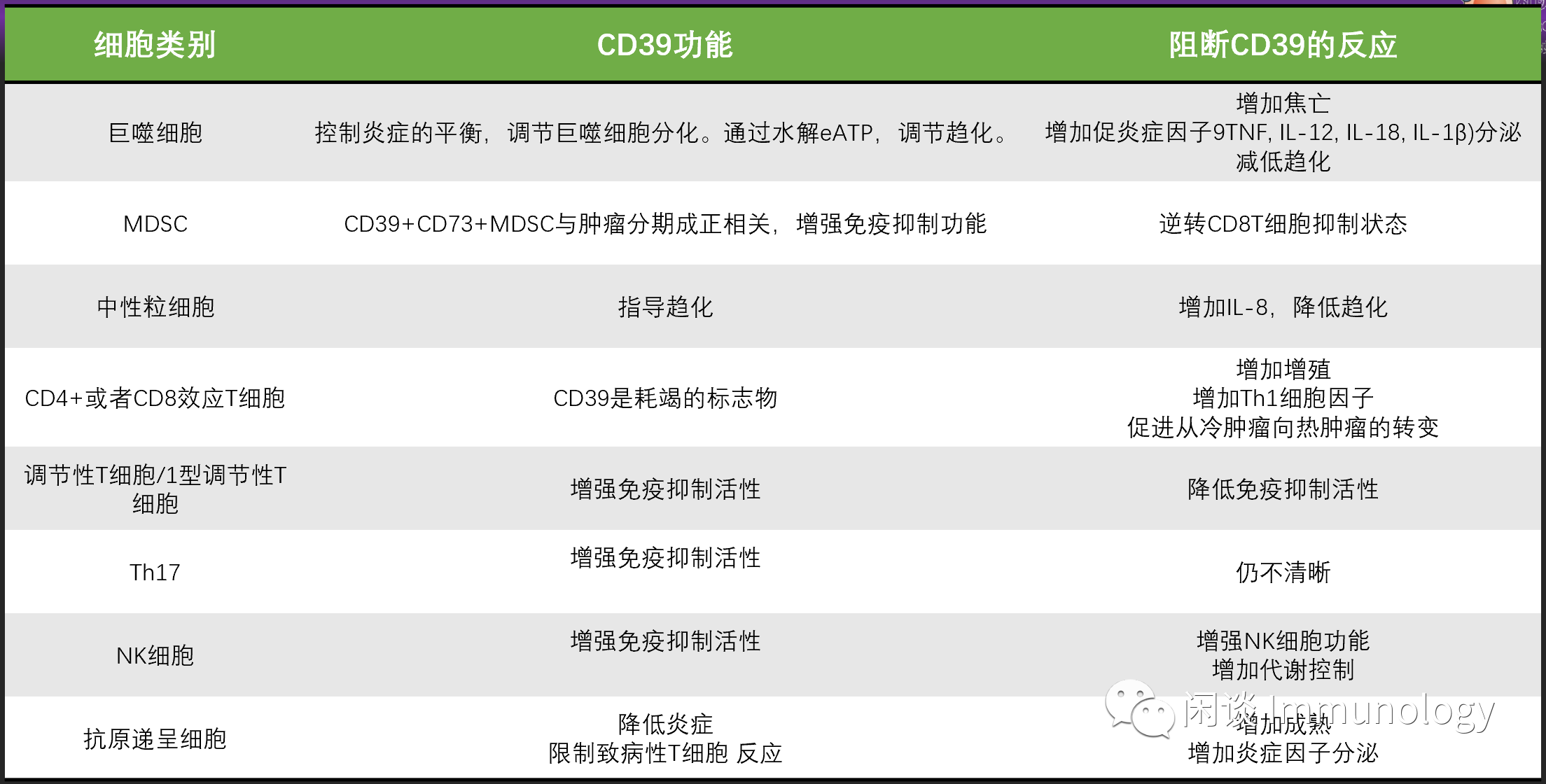
引起CD39表达上调的因素:组织损伤,缺氧,组织重塑:上皮间充质转换,慢性炎症,耗竭T细胞,芳香烃受体(AHR),IL-27信号,细胞死亡/炎症小体介导的焦亡,肿瘤细胞。上调CD39,清除eATP引起的共刺激信号,抑制免疫。
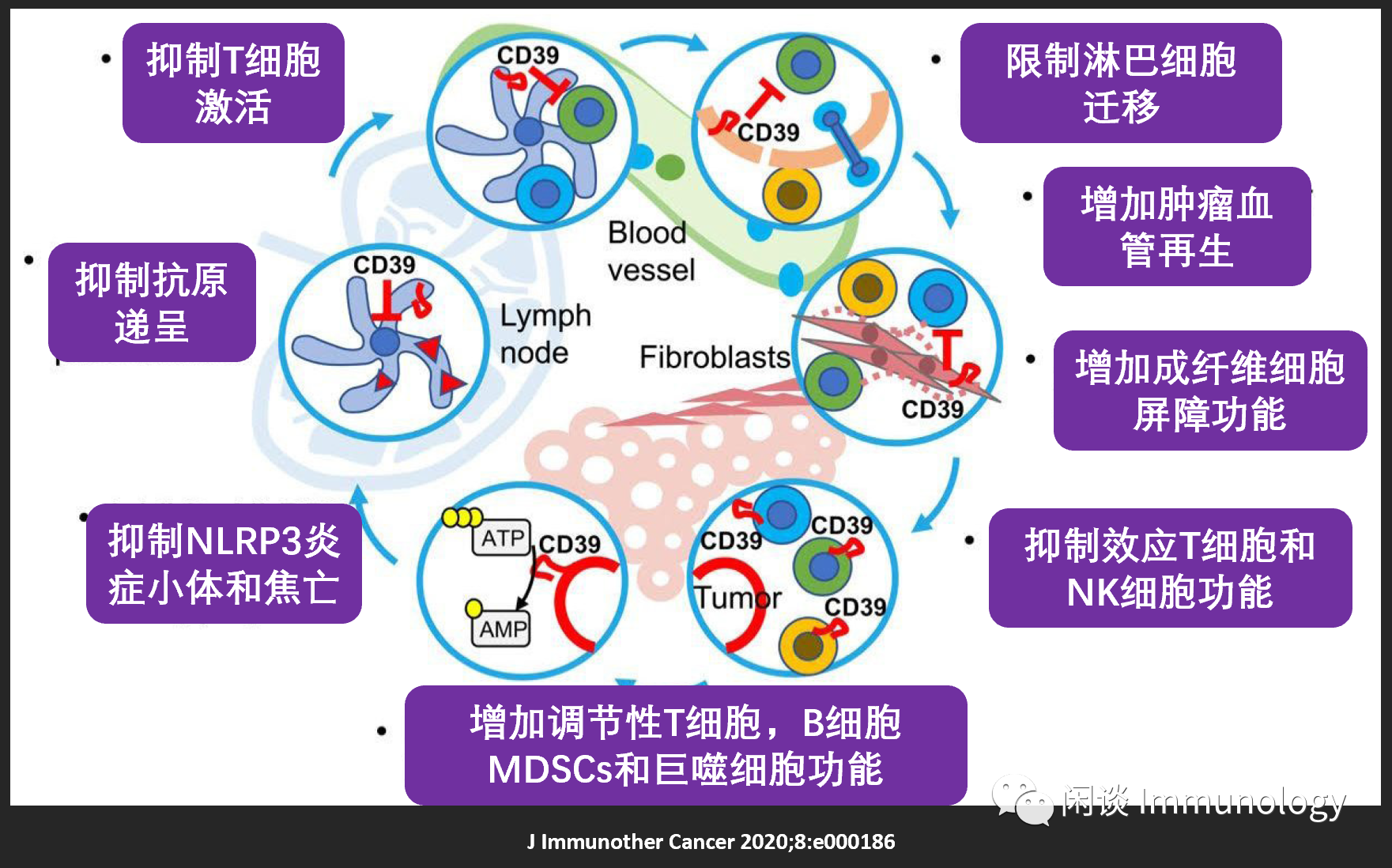
肿瘤微环境中各种细胞(血管内皮细胞,成纤维细胞,NK细胞,巨噬细胞,调节性T细胞,肿瘤特异性T细胞),均高表达CD39。
CD39功能列表
CD39与肿瘤免疫
CD39抗体抗肿瘤机制
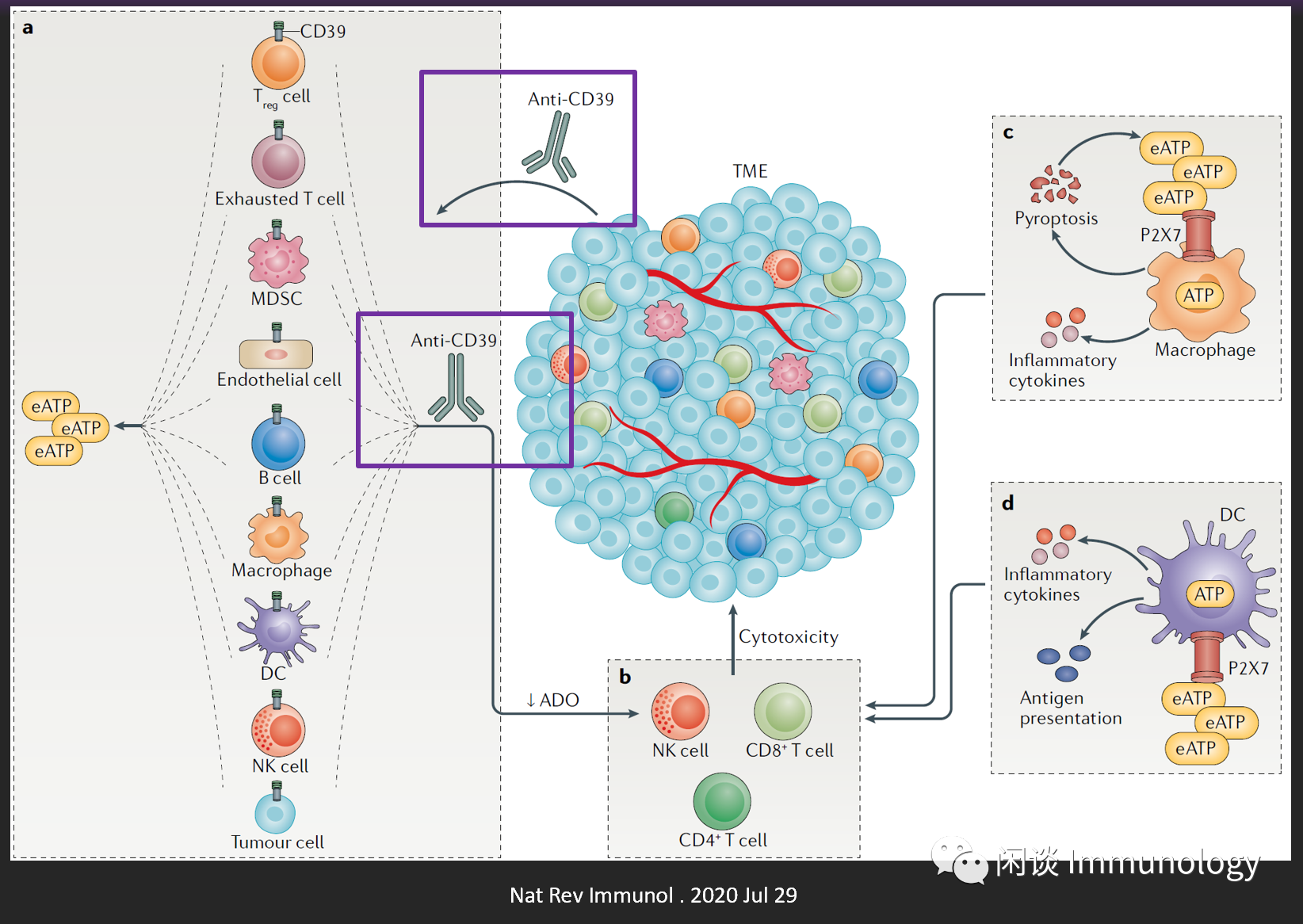
肿瘤微环境中各类细胞均表达CD39,包括T细胞,耗竭T细胞,MDSC,内皮细胞,B细胞,巨噬细胞,NK,DC,肿瘤细胞。
缺氧,细胞死亡(可以是免疫细胞杀死的,和自然死的等),细胞损伤,均会释放eATP,从而激活CD39。
CD39抑制剂(抗体等)阻断此过程,引起eATP水平升高,ADO(accumulation of adenosine,腺苷累积)降低,从而防止各种驻留和浸润的免疫细胞的免疫抑制(如 表达A2A和/或A2B受体的NK细胞和T细胞)。
d.增加的eATP,激活髓系细胞的P2X7,引起炎症小体的形成,促炎症因子(IL-1&β;,IL-18)等的释放,增强T细胞和NK细胞的细胞毒功能。也可以诱导P2X7+巨噬细胞的焦亡。
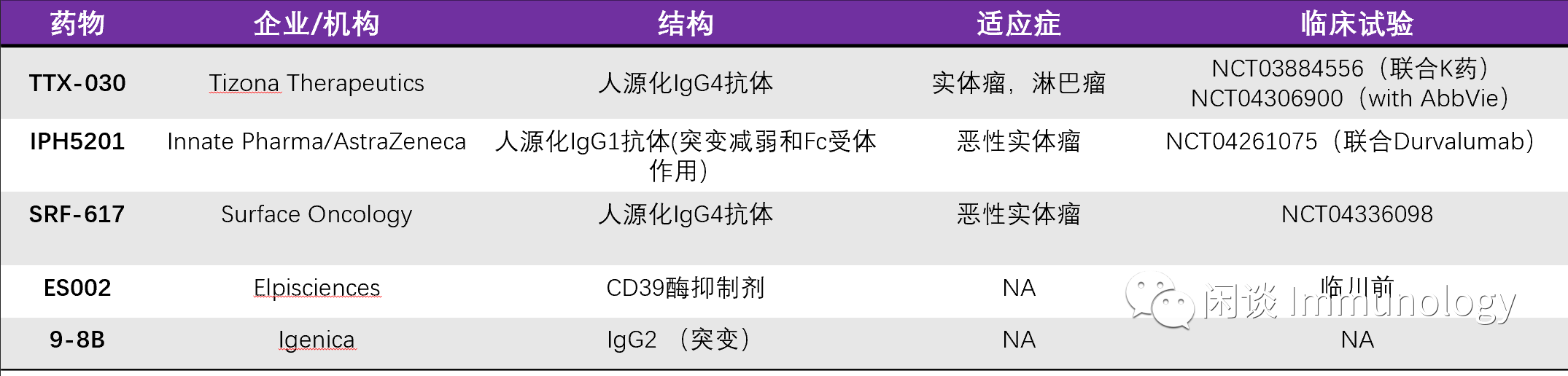
CD39抗体药物
进入临床试验阶段的CD39抗体,多与其他免疫检查点抑制剂联合使用。
参考文献
Achim K Moesta , Xian-Yang Li , Mark J Smyth,Targeting CD39 in cancer,Nat Rev Immunol . 2020 Jul 29
Enjyoji, K. et al. Targeted disruption of CD39/ATP diphosphohydrolase results in disordered hemostasis and thromboregulation. Nat. Med. 1999,5, 1010–1017
David Allard et al,On the mechanism of anti-CD39 immune checkpoint therapy, J Immunother Cancer 2020;8:e000186
Takenaka, M. C. et al. Control of tumor- associated macrophages and T cells in glioblastoma via AHR and CD39. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 729–740 2019).
Allard, B., Longhi, M. S., Robson, S. C. & Stagg, J.The ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73: novel checkpoint inhibitor targets. Immunol. Rev. 2017,276, 121–144
Li, X. Y. et al. Targeting CD39 in cancer reveals an extracellular ATP- and inflammasome- driven tumor mmunity. Cancer Discov. 9, 1754–1773(2019).
来源:闲谈 Immunology 2020-08-27