应对肿瘤相关性恶性呕吐,你学会(fei)了吗?
众所周知,在肿瘤的治疗过程中,恶心、呕吐是常见的不良反应。严重的恶心、呕吐不光会导致脱水、电解质紊乱、伤口裂开、食管黏膜撕裂,还会导致自理能力下降、功能性活动受限、营养缺乏、焦虑、体力状况降低、治疗耐受性降低等严重后果。临床上约30%的恶心、呕吐未获得满意控制,其显著困扰和影响患者的生活质量。为此,本文就止吐药物进行了相应盘点。
01
常用止吐药物的分类、主要机制和代表药物

02
常用抗肿瘤药物的致吐性分级及相应预防措施
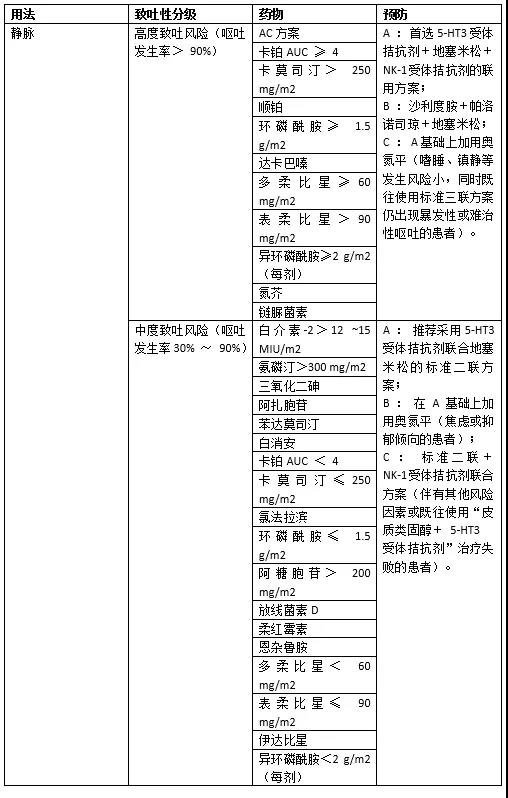

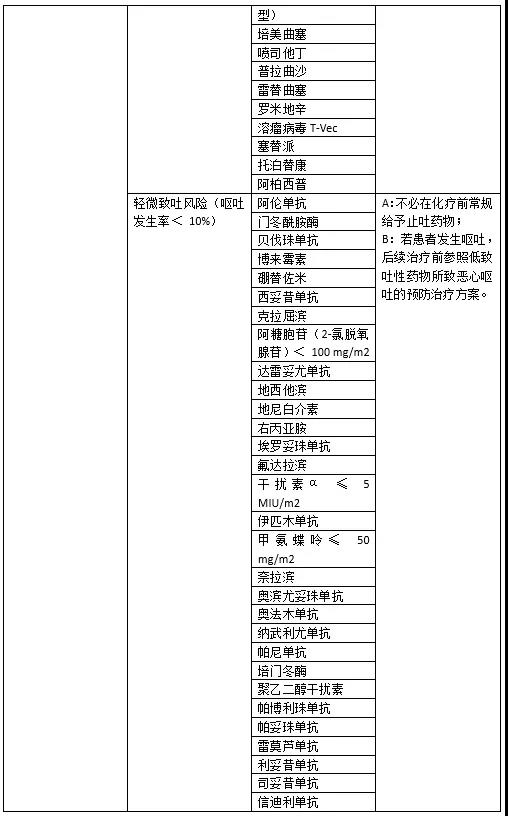
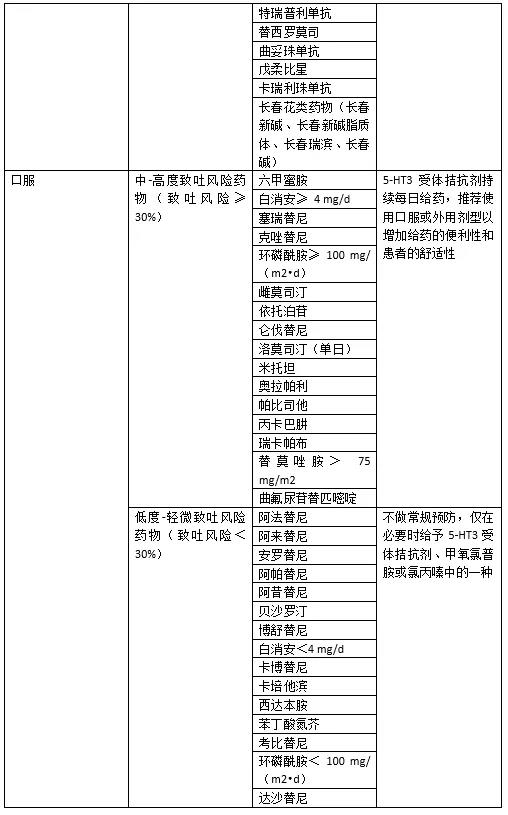
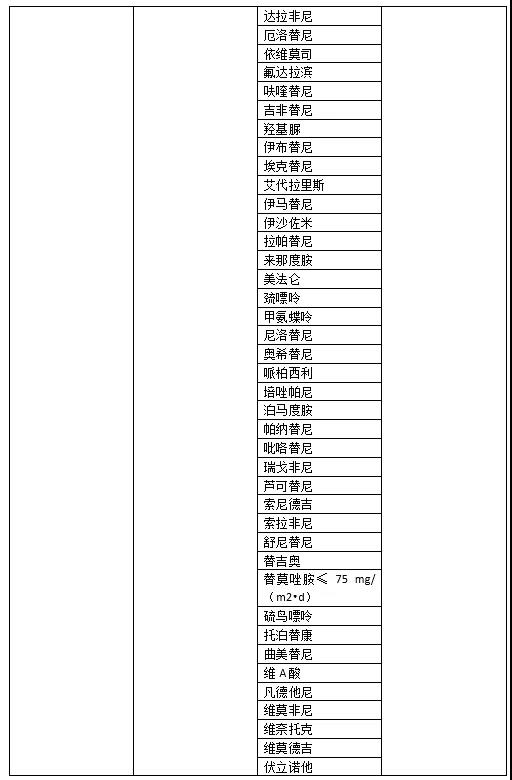
03
特殊类型恶心呕吐的预防
1)多日化疗所致恶心呕吐:
A :标准治疗推荐5-HT3受体拮抗剂联合地塞米松,通常主张在化疗全程使用5-HT3受体拮抗剂,地塞米松应连续使用至化疗结束后2~3d;
B :对于高致吐性或延迟性恶心呕吐高风险的多日化疗方案,可以考虑加入NK-1受体拮抗剂,NK-1受体拮抗剂的使用最多可延续至化疗第7天;
C :复方奈妥匹坦/帕洛诺司琼胶囊兼具NK-1受体拮抗剂和5-HT3受体拮抗剂的作用机制,且使用方便,在多日化疗高致吐方案中可考虑使用。
2)预期性恶心呕吐:
发生于曾接受化疗的患者,在下一次化疗前即出现恶心呕吐,其发生常与既往化疗不愉快的体验相关。最有效的方法是在每周期化疗时给予最佳止吐治疗,防止呕吐的发生。
04
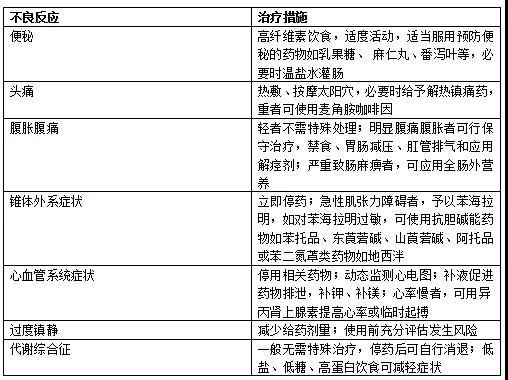
止吐药物不良反应及其处理
参考文献:
[1]McDonagh M, Peterson K, Thakurta S. Consideration of evidence on antiemetic drugs for nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy or radiation therapy in adults[J/OL]. Rockville(MD); 2010.[2019-08-30].https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25473695.
[2]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Antiemesis. V ersion 1.2019[OL]. (2019-02-28)[2019-8-30]. ttps://www.nccn.org/professionals/
physician_gls/pdf/antiemesis.pdf.
[3]中国抗癌协会肿瘤临床化疗专业委员会,中国抗癌协会肿瘤支持治疗专业委员会.肿瘤药物治疗相关恶心呕吐防治中国专家共识(2019年版)[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2019,11(11):16-26. DOI:10.12037/YXQY.2019.11-04.
[4]Roila F, Molassiotis A, Herrstedt J, et al. 2016 MASCC and ESMO guideline update for the prevention of chemotherapy- and radiotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting and of nausea
and vomiting in advanced cancer patients[J]. Ann Oncol, 2016, 27(suppl 5):v119-v133.
[5]Hesketh PJ, Kris MG, Grunberg SM, et al. Proposal for classifying the acute emetogenicity of cancer chemotherapy[J]. J Clin Oncol, 1997, 15(1):103-109.
[6] Roila F, Herrstedt J, Aapro M, et al. Guideline update for MASCC and ESMO in the prevention of chemotherapy- and radiot herapy-induced nausea and vomiting: results of the Perugia consensus conference[J]. Ann Oncol, 2010, 21(Suppl 5):v232-v243.
[7]Ng TL, Hutton B, Clemons M. Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: time for more emphasis on nausea?[J]. Oncologist, 2015, 20(6):576-583.